Red rot of sugarcane is a serious fungal disease that affects sugarcane plants. It damages the stalks from inside, reducing sugar content and yield in the tropical and sub-tropical region of world.
First reported in Java in 1893, it is now found in many sugarcane-growing areas around the world, especially in South Asia. In India, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Haryana and Punjab are the sugarcane growing states particularly.
It is also called the “cancer of sugarcane” because of how quickly and badly it harms the crop.
Causal Organism
Red rot is caused by the fungus Colletotrichum falcatum in its asexual stage. Its sexual (teleomorph) stage is known as Glomerella tucumanensis.
Taxonomy:
| Kingdom | Fungi |
| division | Ascomycota |
| Class | Sordaromycetes |
| Order | Glomerellales |
| Family | Glomerellaceae |
| Genus | Colletotrichum |
| Species | falcatum |
Disease Cycle
In nature red rot disease is seed borne as well as soil borne
Infected setts are the primary source of infection and during rainy season secondry infection occur by conidia through rain water and splash .
The fungus survives in infected setts (seed pieces) and in soil as sclerotia
Primary infection begins when these infected setts are planted
During rainy weather, spores splash from infected debris to healthy stalks, causing new lesions
High humidity (85–100 %) and warm temperatures (29–31 °C) favor rapid disease spread

Figure – Disease cycle of red rot of sugarcane
Image source: Disease cycle of red rot of sugarcane
Symptoms
Disease character appear in the field during rainy season in all aerial part of plant, which includes-
- Foliar phase characteristics
- reddish lesions that extend along the midrib and leaf blade,
- having a pale color at the center where the pathogen sporulates,
- producing conidia within acervuli
- stalk phase Characteristics
- In the vascular tissues (in pith), a reddish discoloration can be observed by splitting the stalks longitudinally.
- Acervuli-like black dots emerge close to the nodes
- This leads to repression of sucrose transporters & the inversion of sucrose giving with a sour, alcoholic smell, and reducing the juice quality and cane weight by 29 – 83%.
- Cavities with cottony fungal growth can form inside the stalk, making stems weak and easily broken
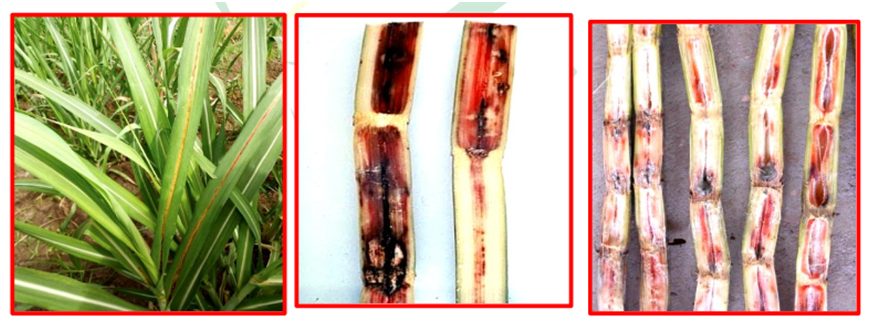
Figure – Symptoms of red rot of sugarcane (source: Arun-Kumar-Red_Rot_Disease_Colletotrichum_falcatum_of_Sugarcane)
Control and Management
- Use healthy setts: Plant only disease-free cane pieces sourced from screened nurseries
- Selection of field with no history of red rot disease.
- ratooning the crop should be avoided.
- Hot-water treatment: Dip setts in 52–55 °C water for 30 minutes to kill the fungus
- Resistant varieties: Grow cane types bred for red-rot resistance where available
- Field sanitation: Remove and burn infected stalks and debris after harvest to lower soil inoculum
- Cultural practices: Maintain balanced fertilizer use and ensure good drainage to reduce plant stress
- Chemical control: Treat setts or soil with fungicides (e.g., carbendazim) when high disease pressure is expected
Read this also
Reference
Red-Rot-Disease-Colletotrichum-falcatum-of-Sugarcane-and-their-Integrated-Management
biologydiscussion.com/plants/plant-diseases/red-rot-of-sugarcane-with-diagram/64325
