Imagine that you have a mixture of different sizes of DNA/RNA in your tube and you want to check what their size is. How can you do it?
One method is described here. After reading this article, you will be able to understand how to do it.
So let’s start..
Table of Contents
What is Agarose Gel Electrophoresis?
Agarose gel electrophoresis is a laboratory technique used to separate DNA fragments based on their size. It is a simple and versatile method that is used in a wide variety of applications, including DNA cloning, DNA sequencing, and genetic analysis.
Aim and Objectives of Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
The aim of agarose gel electrophoresis is to separate DNA fragments into discrete bands based on their size. This can be used to:
- Determine the size of DNA fragments
- Identify and quantify DNA fragments
- Compare DNA samples
- Detect DNA mutations
Principle of Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
Agarose gel electrophoresis works by exploiting the fact that DNA molecules are negatively charged. When placed in an electric field, DNA fragments will migrate towards the positive electrode. The rate of migration depends on the size of the DNA fragment: smaller fragments will migrate faster than larger fragments.
The agarose gel provides a physical barrier that slows down the migration of DNA fragments. The larger the pores in the gel, the faster the DNA fragments will migrate. Therefore, by choosing the appropriate agarose concentration, it is possible to separate DNA fragments of different sizes.
Instrumentation of Agarose Gel Electrophoresis Unit
The basic instrumentation for agarose gel electrophoresis consists of the following:
- Power supply: Provides the electric field that drives the DNA fragments through the gel.
- Electrophoresis tank: Holds the gel and provides a buffer solution that maintains the electric field.
- Gel comb: Creates wells in the gel for loading the DNA samples.
- Gel box: Holds the electrophoresis tank and provides a platform for running the gel.
- UV transilluminator: Used to visualize the DNA bands after electrophoresis.
Requirements for Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
The following materials are required for agarose gel electrophoresis:
- Agarose powder
- Electrophoresis buffer
- DNA samples
- Gel comb
- Gel box
- Power supply
- UV transilluminator
Procedure of Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
- Prepare the agarose gel. This involves melting the agarose powder in electrophoresis buffer and pouring the molten agarose into a gel box.
- Load the DNA samples into the wells of the gel using a micropipette.
- Apply an electric field to the gel. The DNA fragments will migrate towards the positive electrode.
- Run the gel until the DNA fragments have migrated to the desired position.
- Visualize the DNA bands using a UV transilluminator.
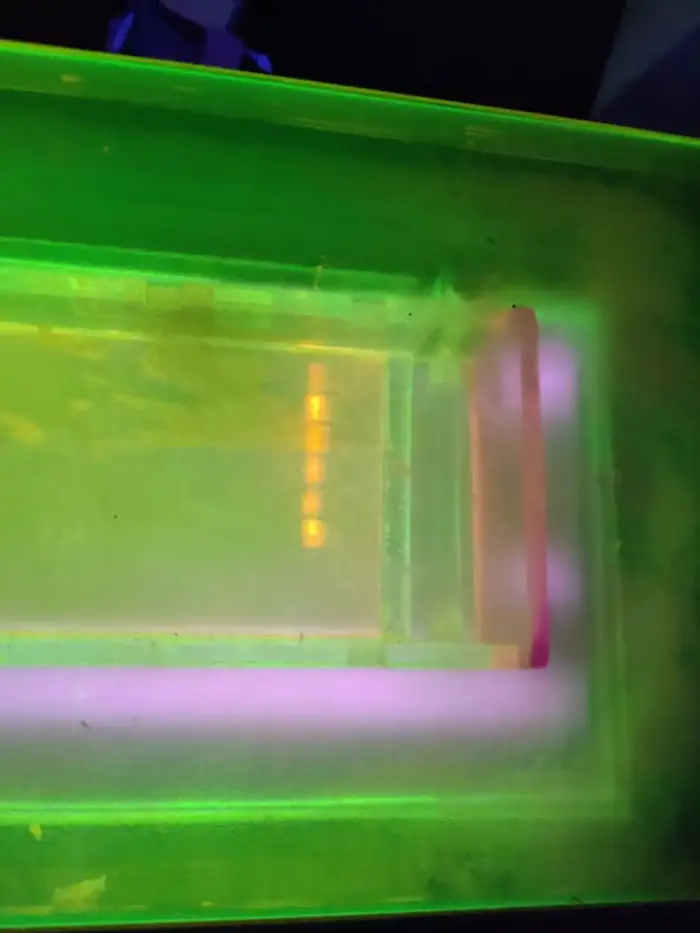
Applications of Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
Agarose gel electrophoresis is used in a wide variety of applications, including:
- DNA cloning: To isolate specific DNA fragments from a complex mixture.
- DNA sequencing: To determine the nucleotide sequence of a DNA fragment.
- Genetic analysis: To identify and quantify DNA mutations, and to compare DNA samples from different individuals.
- Forensic science: To identify individuals based on their DNA profile.
Advantages of Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
Agarose gel electrophoresis is a simple, versatile, and sensitive method for separating DNA fragments. It is relatively inexpensive and easy to perform, and it can be used to separate DNA fragments of a wide range of sizes.
Disadvantages of Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
One disadvantage of agarose gel electrophoresis is that it can be time-consuming, especially for large DNA samples. Additionally, it can be difficult to quantify DNA bands accurately.
Troubleshooting Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
If the DNA bands on your gel are not well-separated, there are a few things you can check:
Make sure that the agarose concentration is appropriate for the size of DNA fragments you are trying to separate.
Make sure that the electrophoresis buffer is at the correct pH and ionic strength.
Make sure that the DNA samples are loaded evenly into the wells of the gel.
Make sure that the electric field is applied for the correct amount of time.
Also read
- PCR principal steps application
- Unlocking the Genetic Marvel: Plasmids – Types, Functions, and Characteristics
Know more detail on electrophoresis.
FAQ
What is the difference between agarose gel electrophoresis and PAGE (polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis)?
Agarose gel electrophoresis is used to separate DNA fragments, while PAGE is used to separate proteins. Agarose is a natural polymer that is extracted from seaweed, while polyacrylamide is a synthetic polymer. Agarose gels are more porous than PAGE gels, which allows them to separate DNA fragments of a wider range of sizes.
What is the best agarose concentration to use for separating DNA fragments of a certain size?
The best agarose concentration to use depends on the size of DNA fragments you are trying to separate. A general rule of thumb is to use a lower agarose concentration for larger DNA fragments and a higher agarose concentration for smallar DNA fragments
Source
- https://link.springer.com/protocol/10.1007/978-3-642-34410-7_5
- Yılmaz, Muhittin, Cem Ozic, and İlhami Gok. “Principles of nucleic acid separation by agarose gel electrophoresis.” Gel Electrophoresis–Principles and Basics 4 (2012): 33.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Agarose_gel_electrophoresis.
